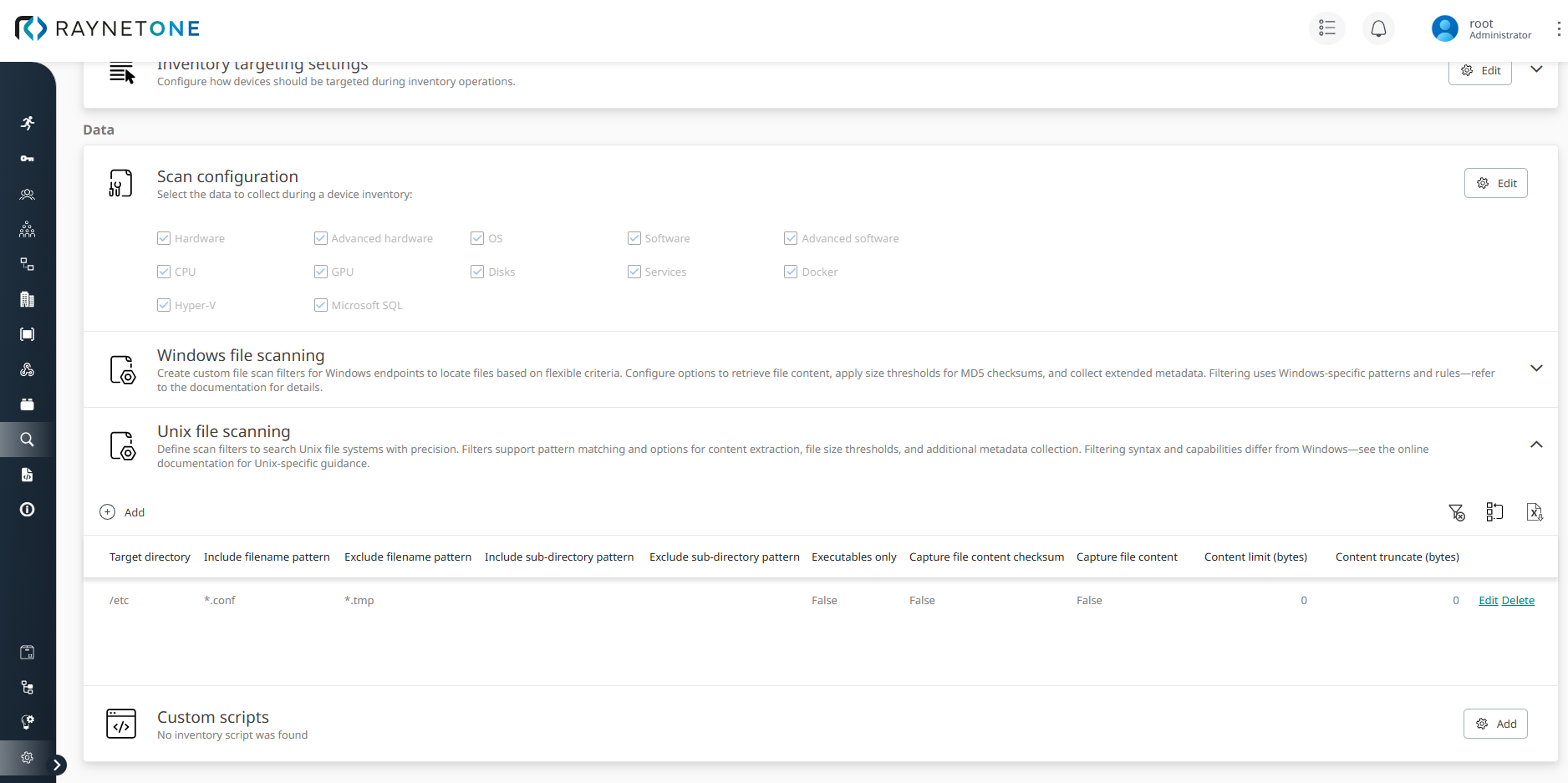
Unix file scanning enables you to create custom search rules that run on Unix/Linux endpoints during Zero-Touch inventory scans. These rules help detect file-based evidence for software installations or system configurations that standard inventory methods may miss. The configuration is centralized in the Unix file scanning table, accessible via Configuration > Scan configuration in Raynet One.
Unix file scan specification parameters
To add a new rule, click Add scan. Define each search filter using the following parameters:
•Target directory: Starting point for the recursive search. (Default: /).
•Include filename pattern: Glob pattern for files to include (e.g., *.conf).
•Exclude filename pattern: Glob pattern for files to exclude (e.g., *.tmp).
•Include sub-directory pattern: Glob pattern to include specific subdirectories.
•Exclude sub-directory pattern: Glob pattern to exclude subdirectories.
•Executables only: Limit results to executable files only. (Default: false).
•Capture file content checksum: Compute and store an MD5 checksum of file content. (Default: false).
•Capture file content: Embed file content in inventory results. (Default: false).
•Content limit (bytes): Maximum file size for content capture. Value 0 means no limit (set to 0, the system falls back to a global default (typically 1024 bytes)). (Default: 0).
•Content truncate (bytes): Maximum bytes stored from file content. Excess bytes are discarded (only the beginning of the file is retained). Value 0 means no truncation, no content is truncated (full file up to limit). (Default: 0).
The search is recursive by default, starting from the specified Target directory and including all subdirectories (unless restricted by include/exclude sub-directory patterns).
Filename and sub-directory patterns follow standard glob syntax (e.g. *, ?, [abc]).
|
Note: |
Practical examples:
Broad Executable Discovery
Target directory: /etc
Include filename pattern: *.conf
Exclude filename pattern: *.tmp
Include sub-directory pattern:
Exclude sub-directory pattern:
Executables only: False
Capture file content checksum: False
Capture file content: False
Content limit (bytes): 0
Content truncate (bytes): 0
When multiple Unix file scan rules are defined, they are executed in parallel during an Inventory scan. Raynet One automatically deduplicates matching files based on their full path, ensuring that each file appears only once in the results while retaining the richest available metadata from all applicable rules.
Once added, these custom Unix file scan rules are automatically applied during a successful Inventory scan. The matching files are then filtered according to the defined patterns and options, with the results visible in the Raynet One platform. For examples of how these results appear in practice, see the section Viewing scan results.