The Edit Installer dialog for third party installers consists of two different tabs.
General
In the General tab of the Edit Installer dialog for third party installers the basic commands for the installer can be configured.
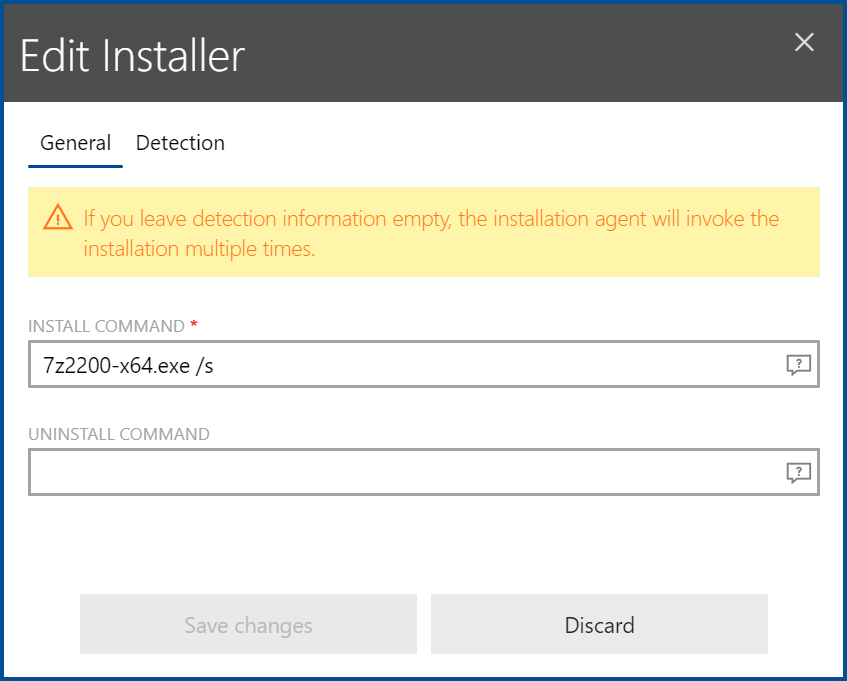
The following commands can be specified in the General tab.
•INSTALL COMMAND: This field can be edited in order to specify how to install the application and pass the appropriate command-line arguments to the application. By default, it contains the name of the file without further command-line arguments. An example would be readerdc_de_xa_crd_install.exe for a German version of the Adobe Acrobat Reader.
•UNINSTALL COMMAND: Enter a command to uninstall the package into the UNINSTALL COMMAND field. The command should be an exact match of the command that would be entered into the command-line interface of the operating system. If using environment variables, to define an uninstall command, the variables need to be used in a specific way. For example, if the %temp% variable should be part of the command. It needs to be used as $(TEMP).
The following table is a list of variables that can be used.
Variable |
Usage |
Default Path |
|---|---|---|
%SystemDrive% |
$(SystemDrive) |
C:\ (The operating system drive) |
%SystemRoot% |
$(SystemRoot) |
C:\Windows |
%WINDIR% |
$(WINDIR) |
C:\Windows |
%HOMEDRIVE% |
$(HOMEDRIVE) |
C:\ (The operating system drive) |
%HOMEPATH% |
$(HOMEPATH) |
C:\Users\<username> |
%USERPROFILE% |
$(USERPROFILE) |
C:\Users\<username> |
%APPDATA% |
$(APPDATA) |
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming |
%ALLUSERSPROFILE% |
$(ALLUSERSPROFILE) |
C:\ProgramData |
%PROGRAMFILES% |
$(PROGRAMFILES) |
C:\Program Files |
%PROGRAMFILES(x86)% |
$(PROGRAMFILES(x86)) |
C:\Program Files (x86) |
%PROGRAMDATA% |
$(PROGRAMDATA) |
C:\ProgramData |
%TEMP% |
$(TEMP) |
C:\Users\<Username>\AppData\Local\Temp |
%LOCALAPPDATA% |
$(LOCALAPPDATA) |
C:\Users\<Username>\AppData\Local |
%PUBLIC% |
$(PUBLIC) |
C:\Users\Public |
%COMMONPROGRAMFILES% |
$(COMMONPROGRAMFILES) |
C:\Program Files\Common Files |
%COMMONPROGRAMFILES(x86)% |
$(%COMMONPROGRAMFILES(x86)) |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files |
Detection
In the Detection tab of the Edit installer dialog for third party installers it is possible to define information that can be used by RayManageSoft Unified Endpoint Manager in order to detect if the application is already installed on a device.
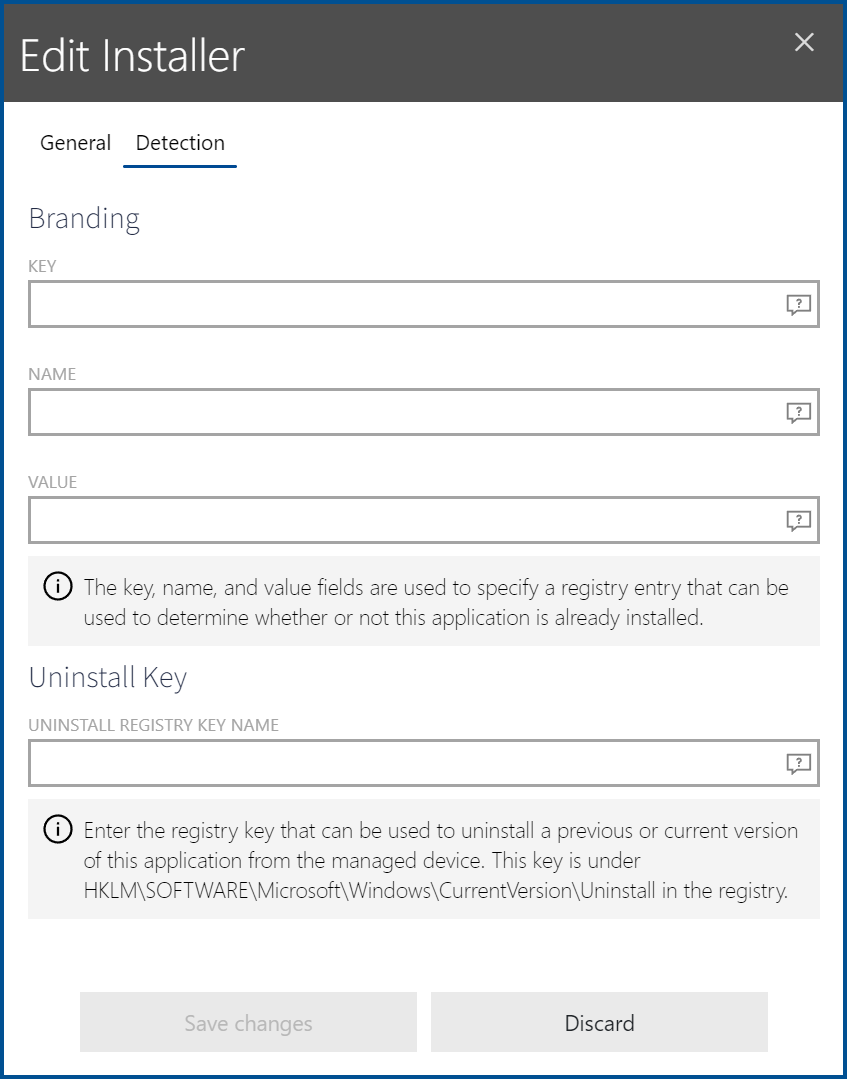
The following information can be specified.
•KEY: In the Key field , the key of the registry hive (below HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE) and the key name of a registry key that can be used to determine whether or not the package is already installed can be specified. For example, if the registry key is in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Adobe\AdobeAcrobat\6.0\Installer the entry in the KEY field should be SOFTWARE\Adobe\Adobe Acrobat\6.0\Installer.
•NAME: In the Name field, the name of a registry entry that is used in conjunction with the contents of the KEY field in order to determine whether or not the package is already installed should be entered. If the name of the registry entry set by the application install is Default, the field is left empty.
•VALUE: In the Value field, the value that is used in conjunction with the contents of the KEY and the NAME field in order to determine whether or not the package is already installed should be entered. An example value would be "C:\Program Files\Adobe\Acrobat 6.0\Acrobat".
•UNINSTALL KEY: This field should contain the registry key that is used to uninstall the package. The uninstall registry key usually matches the GUID of the application set in curly brackets. An example value would be {2453DBC8-ACC4-4711-BD03-0C15353AA3D8}. It is not necessary to enter the whole path, the uninstall registry key is sufficient. It does not matter if the key will have to be in the 32-bit or the 64-bit section of the registry. This will be managed automatically.