Configuring the Windows runner can be a challenge in big corporate network environments. If you have installed the runner on the wrong machine, the server connection can fail. In case of unexpected behavior of the runner, we need to investigate possible error causes.
Let's take a look at various methods of troubleshooting the runner.
Restarting the runner Windows service
This method is good in case the runner is stuck in the disconnected state. Restarting the runner forces it to try a reconnect. The Windows service display name is Raynet One Runner Service. Open the Services window on the machine where the runner is installed on.
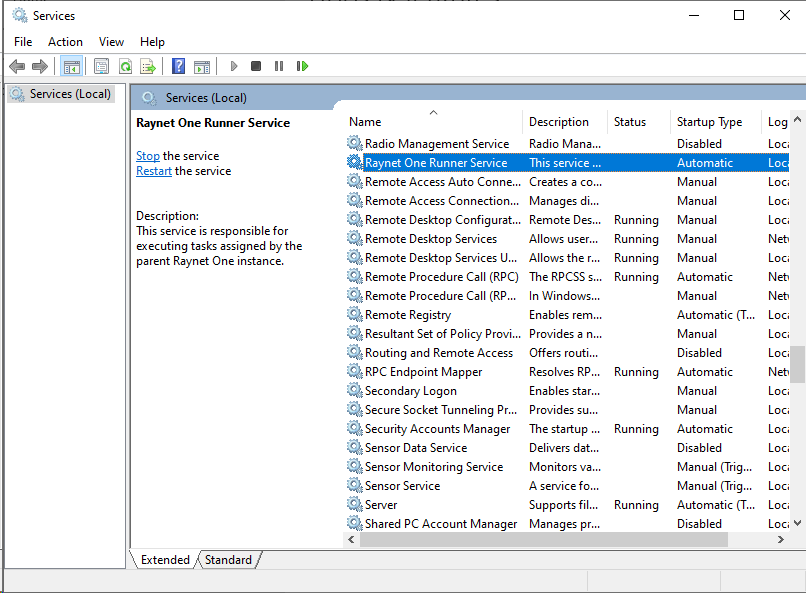
The Services manager of the Windows operating system. On English locale, you can press the Windows key and type in Services, then press Enter to open it. It can be used to restart the runner service.
Select the runner service and click on the blue Restart link to the left above the service description. This causes a shutdown and subsequent start of the runner application. Check the web interface again to see whether the connection problem has been resolved.
Alternatively, you can execute the Windows command sc restart RaynetOneService using the command prompt.
Executing the runner through the Windows command prompt
If you are experiencing any kind of difficult problem with the runner, be it due to misconfiguration or program fault, it may be a good idea to investigate the live runner log. The runner writes its log entries directly into the standard output. When opened through the Windows command prompt, the log is written directly into the command prompt, allowing you to easily trace current runner operation.
Be sure to be logged in as administrator account of your domain network or any equally authorized role to perform runner operations in your environment. Proper runner functionality may depend on the authorization level of the Windows account used to execute the runner.
Before manually executing the runner through the Windows command prompt, always check for another instance of the runner already executing. Most likely, the runner service is already executing. Open the Windows services manager and stop the Raynet One Runner Service. Then proceed with the steps for manual execution.
1.Navigate to the runner installation folder. By default, the runner is installed into C:\Program Files (x86)\Raynet\Runner\ (English locale).
The Windows 10 File Explorer with the runner installation directory open. You can find the main runner application files in this folder.
2.Open a command prompt in this folder. You can click into the URI bar, type in cmd and hit the Enter key.

Typing into the URI bar of the Windows 10 File Explorer allows you to launch programs whose current directory is set to the location of the File Explorer's file-system view.
3.Type in raynet.one.runner.service and hit the Enter key. This will execute the runner manually along with visible logging entries directly in the terminal application. You can find useful troubleshooting information this way.
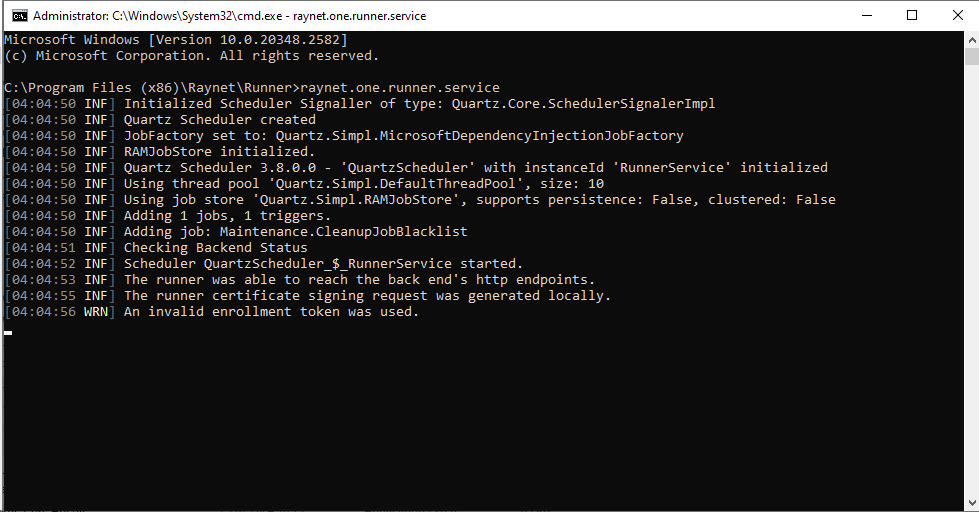
The Windows runner's log. It shows valuable information for troubleshooting. The last log entry is a warning about the use of an invalid enrollment token. In this case, you should try reinstalling a new runner from the web interface. Many log entries are recurring and easy solutions are available. Getting familiar with the runner's logging capabilities is recommended.