In order to collect, normalize, enrich and display available data in your managed environment, you need one or more software deployments of a so-called runner. Depending on the OS, devices and databases in your IT landscape, you can always choose between a Windows runner (available as .MSI file) and a non-Windows, Docker-container-based runner which you can apply for both macOS and Linux environments. Besides, you have the option to deploy the non-Windows runner (also called Cloud Runner) along the system itself.
What is a runner?
The runner is the secure entryway into your IT landscape opened for Raynet One discovery and inventory operations. This software is silently waiting for job requests by the system. Plugins define its capabilities. Multiple runner versions may reside in parallel in your networks, each operating and reporting in a different way. By default, the runner initiates the IP network connection channel, keeping it connected and alive with little passive bandwidth usage. Runner activity is logged on the runner's device and web interface. Various runner configuration options exist inside of the appsettings.json file located in the runner installation folder. They are related to connectivity and technical troubleshooting. There are alternative ways to specify runner application configuration. Runner configuration related to job execution is set in the web interface instead (instrument log level, authorization).
Content of the following chapters
The following chapters concentrate on the initialization of new runners into the platform. They focus on downloading and installing the Windows runner. Runners are either available in the Self-service portal (with video instructions) or under the Runners tab directly on the platform. Learn how to properly expand your IT management reach by carefully studying the steps of runner initialization.
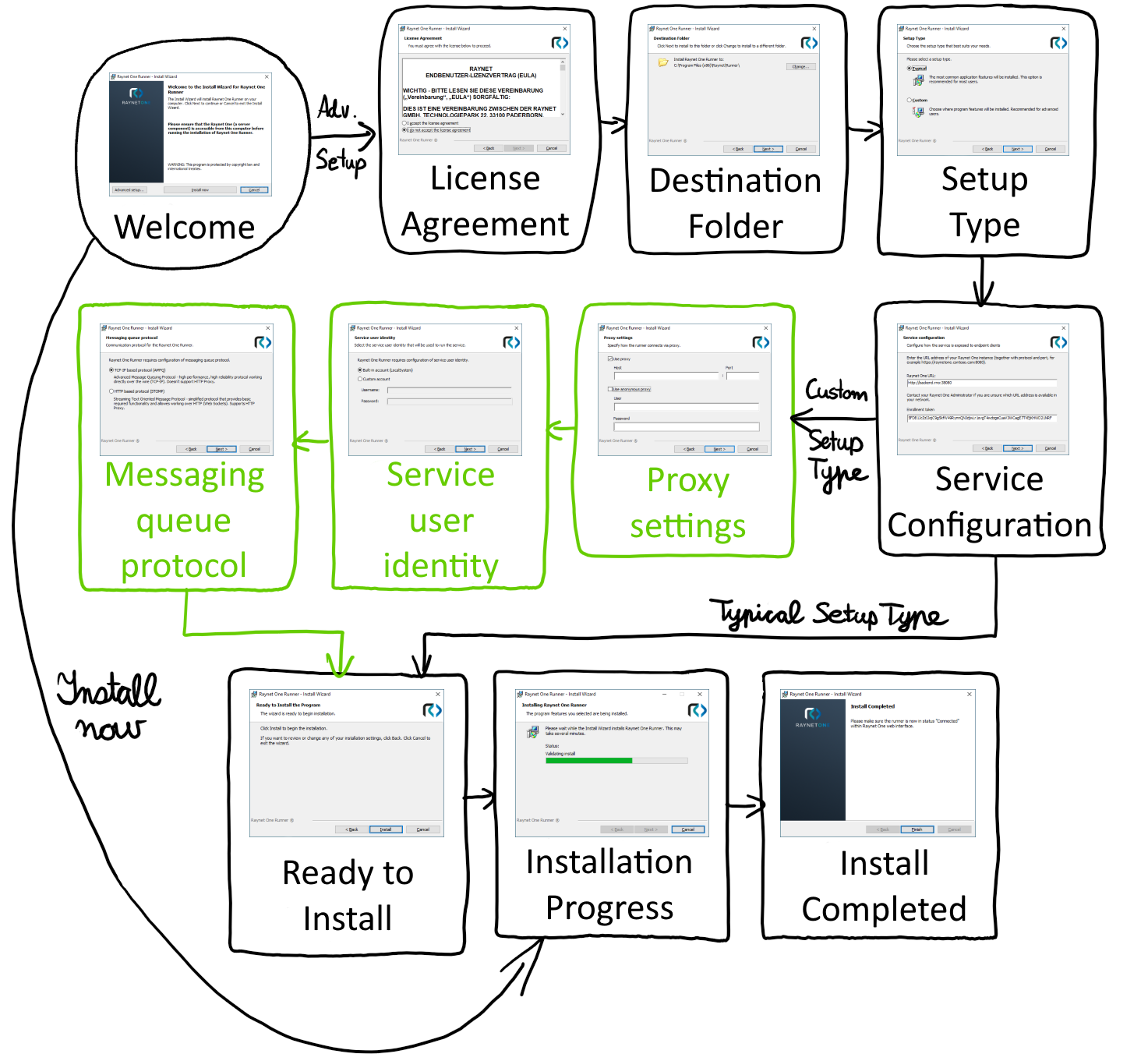
Runner MSI installation sequence