RayFlow has an ability to clone tasks between projects. The Project to which the cloned task belongs can be called the source project and the project to which this task is being cloned can be called the target project. To be able to clone tasks a mapping between the datafields of the target and the source project has to be established. This part of the document describes how this mapping can be achieved.
Before starting with the mapping of datafields, a user needs to select the source project(s) from where the tasks will be cloned. This is done via the Projects settings of the RayFlow Administration feature. More details on this can be found in the Projects chapter of this document.
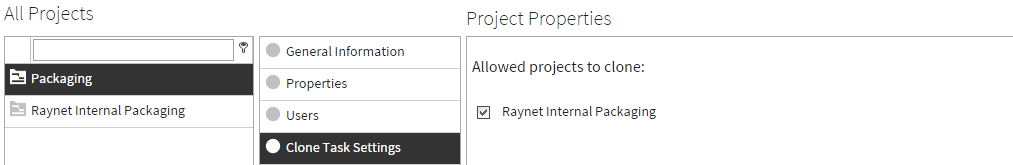
After selecting the source project(s) for the package clone go to the Configuration -> Clone Mappings page to create this mapping. It is important to note that selecting a source project for a task cloning will only allow cloning packages from that project to the target project and not vice-versa.
Clone Mappings Interface
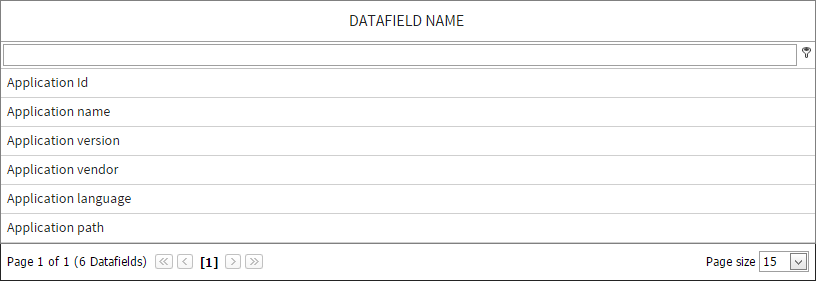
The Clone Mappings interface is a dynamic area which gets extended by the new selection of source projects for task cloning. When no source project is selected only the datafields from the target project are shown. A user can use the search field on top of the list to filter these datafields.
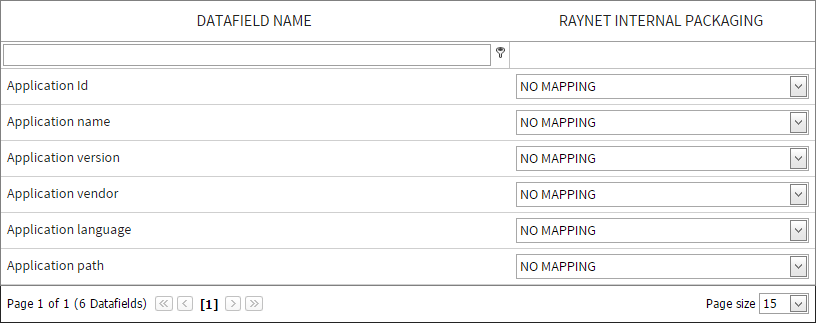
As soon as a source project is selected for task cloning, the source project is added to the interface.
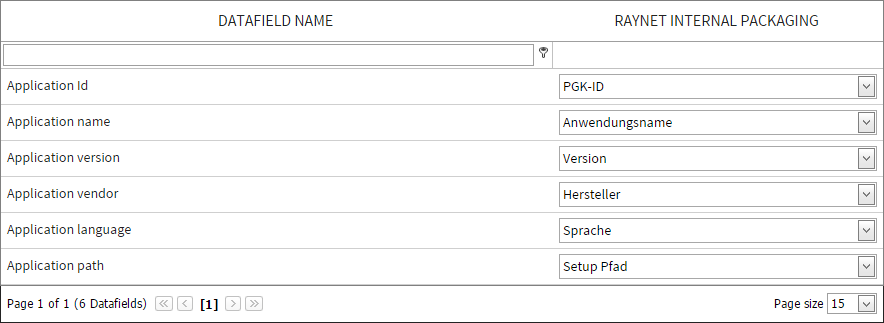
Mapping of Datafields
A map is created between a datafield of the target project to one of the source project. While task cloning, this map tells RayFlow to clone information from the cloned task to the specific datafield in the target project.
Datafields from the source target project are shown under the DATAFIELD NAME column header. Next to each of the datafields there is a drop down list. This drop down list contains datafields of the source project. Simply select the source datafield for each of the target datafields from the drop down list.