Filter step takes one value as input and produces another table with the same schema, but with the same or lower number of rows, based on filter conditions (subtraction).
The simplest definition has the following form:
{
"steps":
[
{
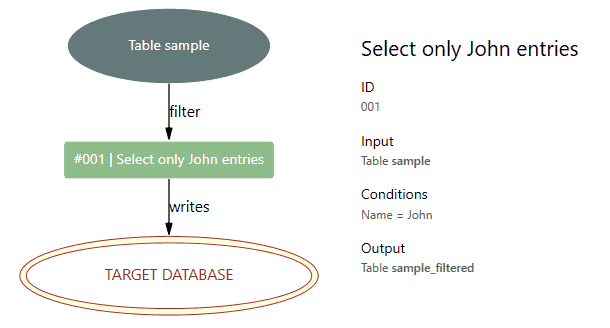
"id": 1,
"name": "Select only John entries",
"target": "sample",
"source": "sample_filtered",
"type": "filter",
"conditions":
[
{
"Name": "John"
}
]
}
]
}
Source is by default optional, meaning that the table does not have to be existing. If the table is missing, the step will not be executed and its target table will not be written. There is a way to define that the source is required, in which case in case of a missing source table the step will fail and report an error. More information about setting up required steps can be found in the following chapter: Optional and required tables.
Example
Given the following table Table_sample:
Name |
Value |
|---|---|
Marcin |
123 |
John |
456 |
Josh |
abc |
John |
aaa |
And the following JSON:
{
"id": 1,
"type": "filter",
"name": "Example of filtering",
"source": "Table_sample",
"conditions": [
{
"Name": "John"
}
],
"target": "TargetTable_Filtered"
}
The following result table TargetTable_Filtered is expected:
Name |
Value |
|---|---|
John |
456 |
John |
aaa |