This section allows you to manage dependencies between tasks. Task dependencies ensure that a task will not start until all its dependent tasks have completed successfully. A task will be prevented from starting if:
•One or more of its dependencies are currently running
•One or more of its dependencies are currently actively writing data to the back-end
•Any of its dependencies is currently on hold because its own dependencies have not yet been satisfied
Managing Dependencies
You can view and manage task dependencies in the Dependencies tab of the task details view. This tab provides two visualization modes: list view and graph view.
List View
The list view displays all task dependencies in a table format, showing detailed information about each dependent task including its status and last run time.
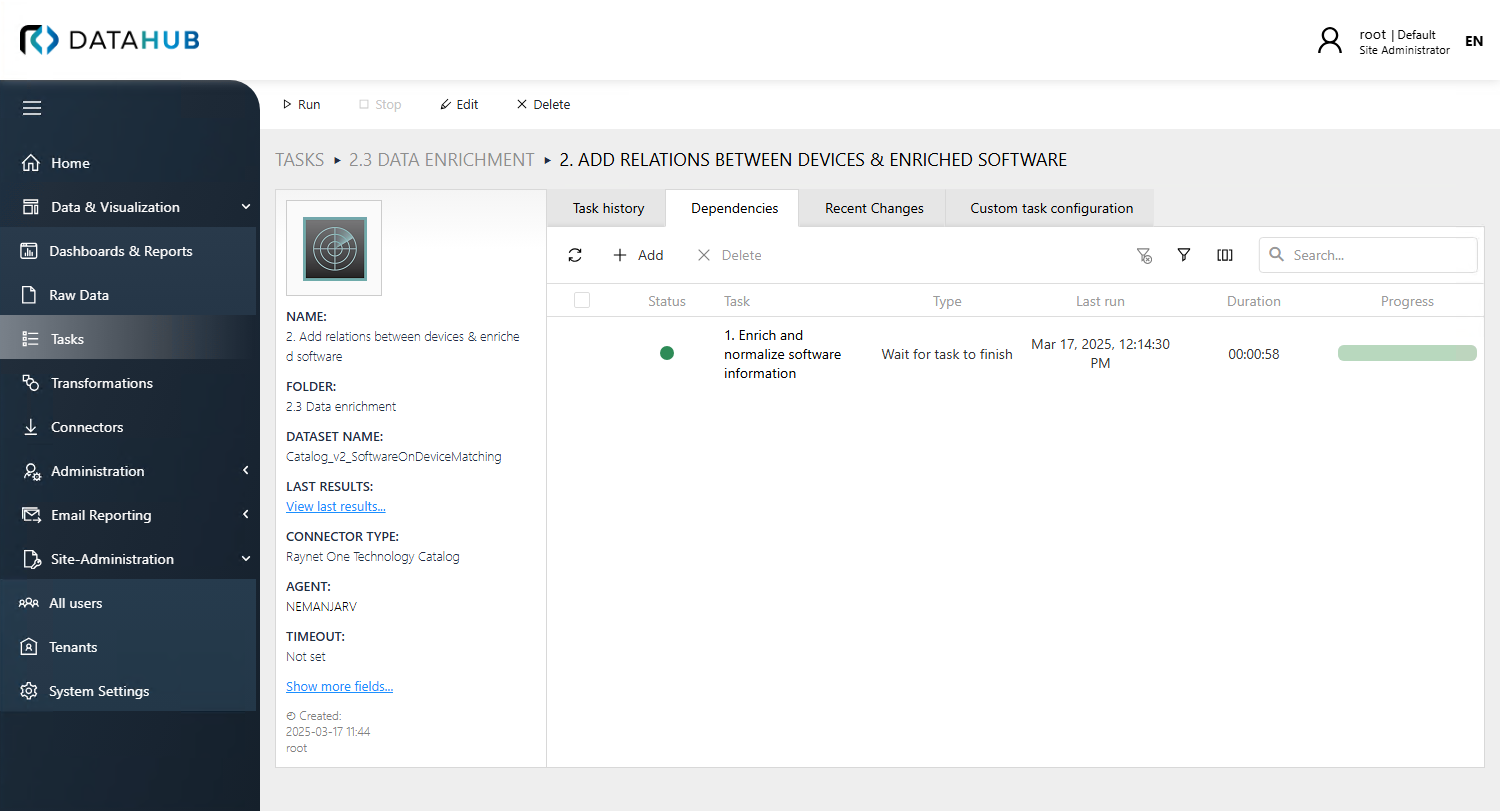
To add a task dependency, press the Add button and select the required task from the list. You can also remove previously set dependencies by selecting them and pressing the Remove button.
Graph View
The graph view provides a visual representation of task dependencies, showing the relationships between tasks as a directed graph. This view helps you understand complex dependency chains and identify potential issues in your task configuration.
Switching Between Views
Use the toggle button in the upper right corner of the Dependencies tab to switch between list view and graph view.
Graph View Features
•Visual representation - Tasks are displayed as nodes, with arrows indicating dependency relationships. The graph shows all dependencies recursively, including indirect dependencies.
•Task details - Click on any task node to view detailed information about that task in a popup panel, including its configuration, status, and recent execution history.
•Context menu - Right-click on a task node to access quick actions such as deleting the dependency or opening the task details in a side panel.
•Graph actions - Right-click on empty space in the graph to access options for refreshing the view or adding a new dependency.
The graph view is particularly useful for:
•Understanding complex dependency chains with multiple levels
•Identifying circular dependencies or potential scheduling conflicts
•Visualizing the overall task execution flow in your data collection workflows