The Delta Comparison Feature provides powerful capabilities for tracking and querying data changes in result tables based on temporal events. This functionality enables you to monitor the complete data lifecycle by identifying when rows were created, updated, or deleted.
Overview
The delta feature introduces:
•Time-based filtering: Query rows based on creation or modification timestamps.
•Deletion tracking: Retrieve information about deleted rows including when they were removed.
•Metadata columns: Access additional system-managed columns that track row lifecycle events.
•Change detection: Identify data changes within specific time spans for incremental processing.
Prerequisites
Before using the delta feature, ensure the following requirements are met:
•Primary Key Requirement: Result tables must have a primary key defined. If no primary key is explicitly defined, the system automatically uses the MD5 checksum generated from row values. However, this may result in duplicates and is not recommended for production use.
•Tenant Configuration: The delta feature must be enabled in the tenant settings. See the section below for detailed configuration instructions.
•API Key Permissions: Your API key must have appropriate permissions to access result database tables.
Enabling the Delta Feature
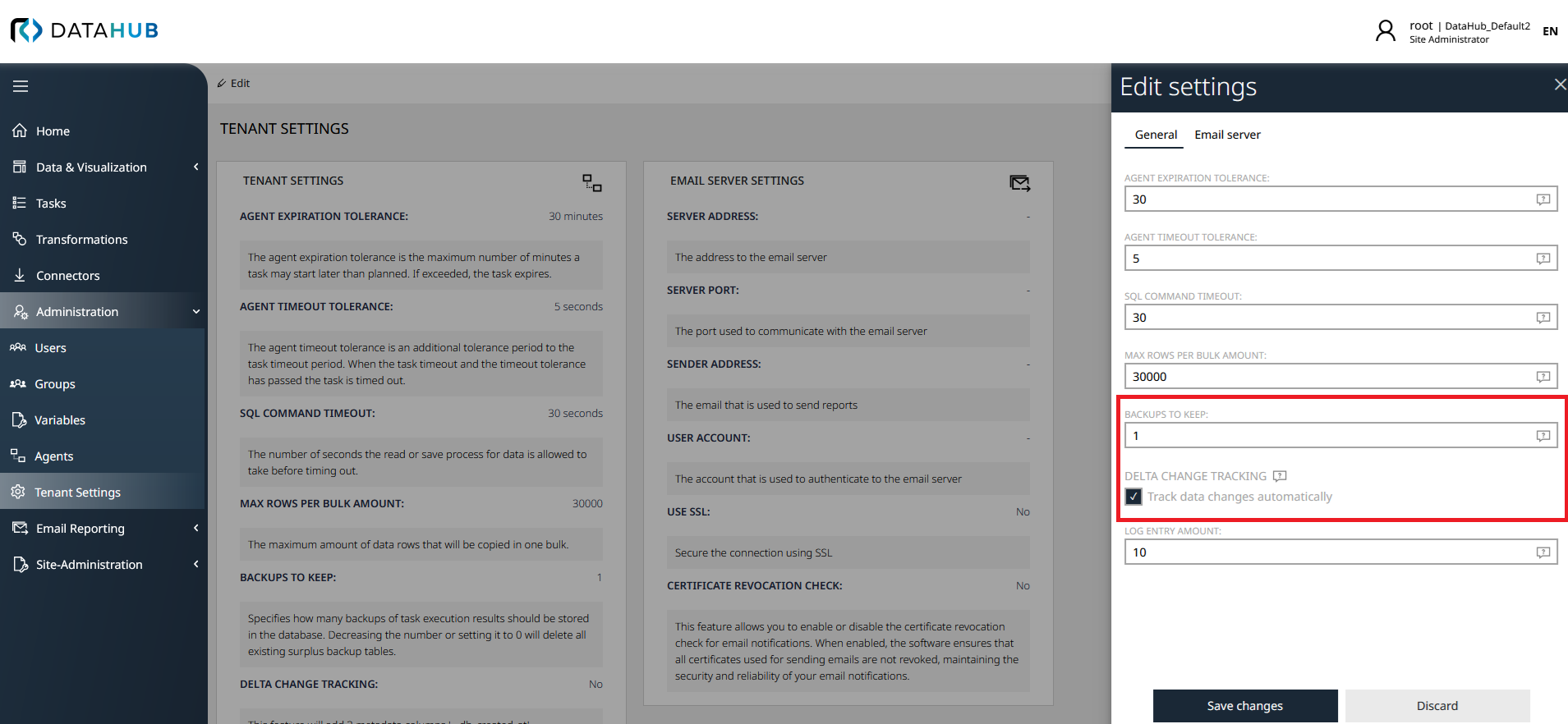
To enable the delta comparison feature for a tenant, two settings must be configured in the tenant settings:
1.Backups to Keep: Set the Backups to keep value to at least 1. This setting determines how many historical snapshots of the data are maintained.
2.Delta Change Tracking: Enable the Delta change tracking checkbox. This activates the tracking of row-level changes including creation, modification, and deletion timestamps.
The following screenshot shows both required settings in the tenant configuration:
|
Important: Always define an explicit primary key on your result tables to ensure accurate delta tracking and avoid potential duplicate issues when using the MD5 checksum fallback. |
Metadata Columns
When the delta feature is enabled, the following system-managed metadata columns become available:
Column Name |
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
__dh_created_at |
DateTime |
Timestamp when the row was initially created in the result table. |
__dh_last_modified |
DateTime |
Timestamp of the most recent modification to the row. |
__dh_md5_checksum |
String |
MD5 hash generated from the row's values, used for change detection. |
__dh_deletion_time |
DateTime |
Timestamp when the row was deleted (available only in deleted rows endpoints). |
API Parameters
The delta feature introduces new parameters that can be used with existing and new API endpoints. All timestamp parameters use ISO 8601 date format.
Parameters for Existing Endpoints
These parameters can be used with the standard table retrieval endpoints to filter results based on temporal criteria:
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
createdSince |
Retrieve only rows created on or after the specified timestamp. Format: ISO 8601 (e.g., "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"). Can be combined with createdUntil to define a time span. |
createdUntil |
Retrieve only rows created before or on the specified timestamp. Format: ISO 8601 (e.g., "2024-01-31T23:59:59Z"). Can be combined with createdSince to define a time span. |
updatedSince |
Retrieve only rows updated on or after the specified timestamp. Format: ISO 8601 (e.g., "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"). Can be combined with updatedUntil to define a time span. |
updatedUntil |
Retrieve only rows updated before or on the specified timestamp. Format: ISO 8601 (e.g., "2024-01-31T23:59:59Z"). Can be combined with updatedSince to define a time span. |
includeMetadata |
When set to true, includes the metadata columns (__dh_created_at, __dh_last_modified, __dh_md5_checksum) in the result set. |
Parameters for Deleted Rows Endpoints
These parameters are used with the new deleted rows endpoints:
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
deletedSince |
Retrieve deleted rows after the specified timestamp. Format: ISO 8601. Can be combined with deletedUntil to define a time span. |
deletedUntil |
Retrieve deleted rows before the specified timestamp. Format: ISO 8601. Can be combined with deletedSince to define a time span. |
includeMetadata |
When set to true, includes the metadata columns (__dh_md5_checksum, __dh_deletion_time) in the result set. |
New API Endpoints
The delta feature introduces new endpoints specifically for retrieving information about deleted rows. For comprehensive documentation on these endpoints, see:
•Getting Deleted Rows (Full Table)
•Getting Deleted Rows (Paged Query)
Advanced Configuration
Advanced configuration options allow fine-grained control over backup and delta computation behaviors.
Table Exclusion (IgnoreTables)
The IgnoreTables setting allows you to exclude specific tables from backup operations and delta computations. This feature is configured in the appsettings.json file within the TasksManagement section.
Configuration Locations:
•TasksManagement → BackupManagement → IgnoreTables: Excludes tables from backup operations.
•TasksManagement → DeltaManagement → IgnoreTables: Excludes tables from delta change tracking.
Wildcard Support:
The IgnoreTables setting supports wildcard patterns for flexible table matching:
•* (asterisk): Matches zero or more characters.
•? (question mark): Matches exactly one character.
Common Use Cases:
•Large matching tables: Exclude catalog matching tables that change frequently but don't require historical tracking (e.g., Catalog_v2-SoftwareTransformationMatching).
•Temporary tables: Exclude intermediate result tables that are regenerated on each task run (e.g., DataTransformation-persistent_inv_raw_generic_Office365).
•External system tables: Exclude connector-specific tables by pattern (e.g., Inventory*, aws*, Office365Data*).
•Upstream version tables: Use wildcards to exclude entire table families (e.g., Catalog_v2-SWUpstreamVersion*).
Example Patterns:
•Catalog_v2-SWUpstreamVersion*: Matches all upstream version tables.
•Inventory*: Matches all tables starting with "Inventory".
•*Matching: Matches all tables ending with "Matching".
•RaynetOneApi-*: Matches all RaynetOne API tables.
|
Important: Tables excluded via IgnoreTables will not have delta metadata columns and cannot be queried using delta-specific API parameters. Carefully consider which tables should be excluded based on your data retention and compliance requirements. |
Custom Column Mappings for Delta Computation
In certain scenarios, result tables may contain automatically generated columns (such as identity columns or auto-incremented IDs) that change on every task execution. This prevents the delta feature from accurately identifying whether a row has truly changed or is simply a re-insertion of the same data.
The custom column mapping feature allows you to override the default delta computation behavior by specifying which columns should be used as keys and which columns should be excluded from the MD5 hash calculation.
Configuration Location:
Column mappings are configured in the appsettings.json file under TasksManagement → DeltaManagement → Tables. Each table can have its own custom configuration.
Column Mapping Types:
Mapping Type |
Description |
|---|---|
KEY |
Defines the column(s) that uniquely identify a row. These columns are excluded from the MD5 hash calculation and are used to match rows across task executions. Multiple columns can be designated as keys to create composite keys. |
IGNORE_FOR_MD5_HASH |
Excludes the column from the MD5 hash calculation used to detect changes. The column is still part of the result set but does not influence whether a row is considered modified. This is typically used for auto-generated identity columns or timestamps that change on every run. |
Filter Conditions:
In addition to column mappings, you can define filter conditions that determine which rows are included in the delta computation. The FilterConditions property accepts an array of conditions that can be combined using logical operators.
Supported Operators:
•= (equals)
•!= (not equals)
•AND (logical AND operator for combining conditions)
Example Configuration: Catalog Software Table
The Catalog_v2-Software table contains an auto-generated softwareId column that changes on every task execution. To enable accurate delta tracking, the configuration specifies:
•softwareId: Marked as IGNORE_FOR_MD5_HASH (excluded from change detection)
•productId and versionId: Designated as KEY columns (used to identify unique software entries)
•Filter conditions ensure only successfully processed rows with valid product and version IDs are included
Example Configuration: Result Devices Table
The DataTransformation-result_devices table demonstrates a simpler configuration:
•device_key: Ignored for MD5 hash calculation
•import_id: Used as the primary key
•No filter conditions (all rows included in delta computation)
|
Best Practice: Define custom column mappings for tables with auto-generated columns to ensure accurate delta tracking. Always test the configuration with sample data to verify that changes are correctly detected and that stable rows are not incorrectly flagged as modified. |
Use Cases
The delta comparison feature is particularly useful for:
•Incremental data synchronisation: Fetch only the data that has changed since the last sync operation.
•Change detection: Identify modifications within specific time periods for audit or compliance purposes.
•Delta processing: Process only new or modified records to improve performance and reduce data transfer.
•Data reconciliation: Compare snapshots from different points in time to identify changes.
•Deletion tracking: Monitor which rows have been removed from result tables and when.
Best Practises
•Define primary keys: Always specify explicit primary keys on result tables to ensure accurate tracking.
•Use time spans judiciously: Narrow time ranges improve query performance and reduce data transfer.
•Combine parameters: Use createdSince with createdUntil to define precise time windows.
•Request metadata selectively: Only include metadata columns when necessary to minimise response size.
•Use paged queries: For large result sets, use paged endpoints to manage memory and network resources effectively.
See Also
•Getting Deleted Rows (Full Table)
•Getting Deleted Rows (Paged Query)
•Getting Table Data (Paged Query)
•Getting Table Data (All Rows)