Unix Zero Touch is an agentless, least-invasive inventory method in Raynet One Scan Engine for remote data collection from supported Unix platforms without installing any persistent agent on the target.
Supported Unix Operating Systems
The Unix Zero Touch inventory method is technically compatible with a wide range of Unix like operating systems as long as an OpenSSH server is available and reachable. However, Raynet One officially supports and recommends the use of currently maintained releases from major vendors. This ensures optimal compatibility and reliable inventory results in enterprise environments.
Operating System |
Supported Versions (as of December 2025) |
|---|---|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux |
•7, 8, 9, 10 |
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) |
•12, 15, 16 |
openSUSE |
•15, 16 |
Debian |
•11, 12, 13 |
Ubuntu |
•22.04 LTS, 24.04 LTS, 25.10 |
Fedora |
•42, 43 |
macOS |
•13, 14, 15, 26 |
Oracle Solaris |
•11 |
AIX |
•7.2, 7.3 |
Older or non-listed versions may still provide functional inventory results via SSH; however, they are not part of the official support scope.
The Remote Inventory for Unix (RIU) component orchestrates the entire process via SSH:
•Initial platform fingerprinting and privilege probing
•Adaptive command execution based on detected OS and available privileges (Principle of Least Privilege)
•Application of defined Execution Contexts (No-Elevation, Elevated-First, etc.)
•Collection and return of normalized inventory data (hardware, software, configuration)
Key technical requirements:
•OpenSSH server running and reachable (port 22/TCP by default; custom ports configurable)
•Valid SSH login credentials (password or - recommended - SSH key authentication)
•For full inventory results (hardware, storage, services, containers, etc. ): the scan account must be allowed to run sudo commands without being prompted for a password.
•Without password-less sudo: automatic fallback to non-privileged commands (limited results).
The scan uses only native, universally available utilities and leaves no files or persistent changes on the target system.
Understanding Pseudo-Terminal (PTY) Allocation and PermitTTY Handling
All commands are executed over an SSH session. A Pseudo Terminal (PTY) is a virtual terminal device created by the target kernel under /etc/ssh/sshd_config to emulate a real physical terminal.
The Zero-Touch Unix scanner requests a PTY from the remote SSH server for reliable command execution (e.g. sudo password prompts). The remote SSH server decides whether or not to allocate a pseudo-terminal (PTY). When a PTY is granted, the scanner operates under optimal conditions. If the server refuses the PTY request, the scanner automatically continues in terminal-less NoVirtualTerminal mode through graceful degradation.
When PermitTTY is set to yes in /etc/ssh/sshd_config, the target server grants the requested PTY.
The kernel dynamically creates a virtual terminal device (e.g. /dev/pts/23 ) and the remote session receives a fully-featured terminal environment ($TERM = xterm-256color or similar). This is the intended and optimal state for Zero-Touch Unix scans.
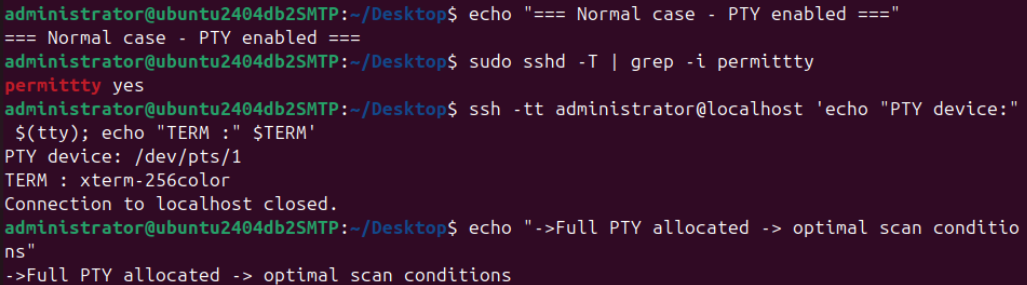
The following live examples were executed on an internal test system (Ubuntu 24.4). The exact output (especially the PTY device number '/dev/pts/XX' and the concrete 'TERM' may vary depending on the target operating system, SSH server configuration, and currently active sessions. These examples are for illustration purposes only and do not guarantee identical results on scanned systems.
The optional instrument setting UseNoVirtualTerminal (default: disabled) is available in Raynet One at Configuration, Plugins, Unix Zero Touch Inventory, Instruments, Zero Touch Unix Device Scan, Settings. When the Use no virtual terminal checkbox is selected, the scanner forces terminal-less NoVirtualTerminal mode operation from the start, even when then target server would permit a PTY.
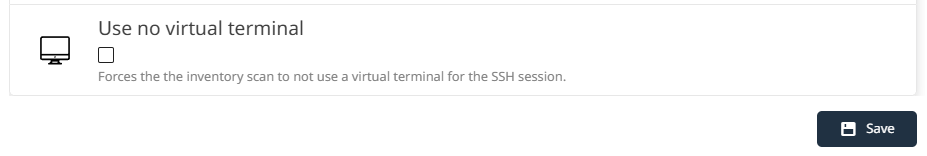
After changing the setting if desired, click Save to apply the configuration.
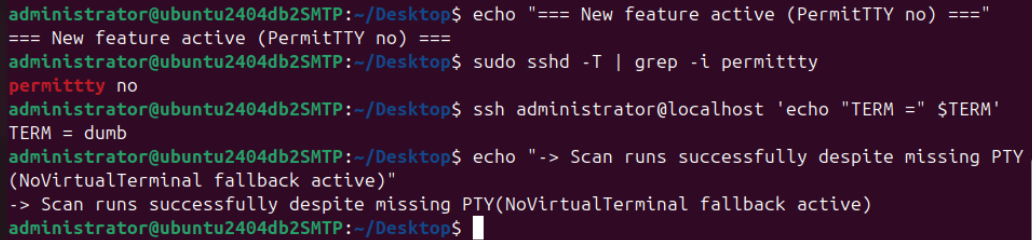
By default the setting is disabled, so the scanner first attempts a normal PTY connection and automatically falls back to NoVirtualTerminal mode through graceful degradation only if PTY allocation is refused (e.g. PermitTTY no in /etc/ssh/sshd_config). In this fallback case the scan continues with only minor limitations.
Regardless of whether a full PTY or terminal-less mode is used, the Zero-Touch Unix scan always relies exclusively on native, universally available system utilities and leaves no files or persistent changes on the target system.
This documentation reflects Raynet One Scan Engine 12.6+ behaviour (Dezember 2025). Individual environments (restricted shells etc.) may require adjustments.
Execution Context Overview
The scanner uses an intelligent Execution Context system to run every command with the minimum required privileges (Principle of Least Privilege). Each command is classified into an Execution Context.
The classification decides:
•Access Method: How the command reaches the target (always SSH command execution or script upload).
•Execution Method: How the command determines privilege elevation strategy (QuickRun, Run, RunTryElevatedFirst, RunTryElevatedLast, RunScript).
•Privilege Elevation: How elevated privileges (sudo) are attempted during execution (Without elevation/ Tried with elevation first/ Tried with elevation last).
The table below defines the Execution Contexts used throughout this documentation:
Execution Context |
Access Method |
Execution Method |
Privilege Elevation |
Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Elevated-First |
•SSH Command Execution |
•RunTryElevatedFirst |
•Tried with elevation first |
•Hardware queries, disk operations, package management, network info, services, containers |
No-Elevation |
•SSH Command Execution |
•QuickRun |
•Without elevation |
•Basic system info, user info, file operations, process listing |
Elevated-Last |
•SSH Command Execution |
•RunTryElevatedLast |
•Tried with elevation last |
•Database queries (SQL Server) |
Script-Execution |
•SSH Command Execution |
•RunScript |
•Without elevation |
•Platform-specific script (e.g., AppleScript on macOS) |
File-Read |
•SSH + File Read |
•QuickRun |
•Without elevation |
•Reading of system configuration and binary files (/etc/*, /proc/*) |
Important: Full inventory depth requires the scan account to have password-less sudo (NOPASSWD) for optimal hardware, storage, service, and container data collection.
Without password-less sudo, the scanner automatically falls back to non-privileged execution using graceful degradation:
•RunTryElevatedFirst commands are executed without sudo - available data is collected with reduced detail
•RunTryElevatedLast commands attempt non-privileged execution first
•QuickRun and No-Elevation commands function normally (they never require elevation)
•The scan process continues uninterrupted, ensuring baseline inventory data is always collected even in highly restricted environments
File-Read is a behavioural flag applied only to No-Elevation (and very rarely Script-Execution) commands that access system files or directories.
It never applies to Elevated-First or Elevated-Last contexts.
How the Scan Works
The Zero-Touch Unix scanner connects to each target system individually via SSH and executes the phases 0 through 8 in strict sequence on that system.
•Phase 0 determines the exact platform, architecture, and available privileges (sudo NOPASSWD or not).
•Phases 1-8 are executed adaptively: only commands that are applicable to the detected OS and permitted by the current privileges are run. Commands requiring unavailable privileges or non-existent binaries are silently skipped (Principle of Least Privilege).
•When Phase 8 is complete, results are returned, the SSH session is closed, and the scanner proceeds to the next target.
•Multiple targets are processed in parallel, with each scan instance executing its own independent Phase 0-8 sequence.
This fully automated, adaptive behaviour is the reason the solution is called Zero-Touch.
The phases described below are executed adaptively; commands are skipped or reordered when required by the target environment or available privileges.
Phase 0: Pre-Check & Capability Validation
Phase 0 is the mandatory, non-privileged first step of every Zero-Touch Unix scan. With one exception (uname -o on AIX/HP-UX, which is attempted with elevation when required ), all commands run under
No-Elevation/ QuickRun.
In a few seconds it reliably determines:
•Exact OS family, version and architecture (uname flags)
•Current user identity and group membership (whoami, id)
•Whether password-less sudo elevation is available and whether the shell is restricted
The separate hostname command is not used; uname -n is preferred because it is universally available, strictly read-only and can be combined with the other uname flags in one call.
By the end of Phase 0, all information required for the adaptive, privilege-aware execution of Phases 1-8 is already available. All commands in Phase 0 run under No-Elevation context (QuickRun). The single exception
is uname -o on AIX/HP-UX when required (Elevated-First).
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
whoami |
•- |
•Get current user |
•All supported platforms |
id |
•- |
•Get user ID info |
•All supported platforms |
uname |
•-n |
•Get hostname |
•All supported platforms |
uname |
•-s |
•Get kernel name |
•All supported platforms |
uname |
•-r |
•Get kernel release |
•All supported platforms |
uname |
•-m |
•Get architecture |
•All supported platforms |
uname |
•-o |
•Get OS type |
•Linux/Unix |
uname |
•-v |
•Get kernel version |
•All supported platforms |
uname |
•-p |
•Get processor type |
•AIX, Solaris |
uname |
•-s | tr 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ' 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz' | sed -e 's/-[0-9\.]*$//' |
•Get normalized OS name |
•All supported platforms |
uname |
•-p | tr 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ' 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz' |
•Get normalized processor type |
•All supported platforms |
echo |
•$PATH |
•Get PATH variable |
•All supported platforms |
Phase 1: System Information
Phase 1 establishes the unambiguous identity of the target system and builds the foundation for all subsequent phases. All commands in this phase use No-Elevation (QuickRun or Standard-Execution) because the required information is publicly readable on every supported Unix platform, no sudo is ever requested.
The phase is divided into two logical parts:
Core System Identification:
The scanner determines the exact operating system family, release, architecture, hostname, domain, and virtualization context (zone/LPAR) using uname variants, normalized pipelines, platform-specific identifiers (zonename, lparstat -i, model, hostid), and the standard release files under /etc (/etc/os-release, /etc/redhat-release, etc. ).
Binary & Path Inventory:
The scanner enumerates all executable files in the standard system paths (/bin, /sbin, /usr/bin, /usr/sbin) and verifies their location, permissions, symlinks, and checksums using find, which, ls, readlink, md5sum, grep, awk, and sed.
This early inventory is critical: the scan process must know which tools are actually available before attempting hardware, storage, or container commands in later sections.
By the end of Phase 1, the scanner has a complete, reliable picture of who the system is and what standard tools it provides, all without requesting elevated privileges. All commands in Phase 1 run under No-Elevation
context.
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
Remote_Files_Accessed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
dnsdomainname |
•- |
•Get DNS domain |
•All supported platforms |
•- |
domainname |
•- |
•Get domain name |
•All supported platforms |
•- |
cat /etc/os-release |
•/etc/os-release |
•Get OS release info |
•Linux |
•/etc/os-release [File-Read] |
cat /etc/lsb-release |
•/etc/lsb-release |
•Get LSB release info |
•Linux |
•/etc/lsb-release [File-Read] |
cat /etc/issue |
•/etc/issue |
•Get system issue |
•Linux |
•/etc/issue [File-Read] |
cat /etc/issue.net |
•/etc/issue.net |
•Get system info |
•Linux |
•/etc/issue.net [File-Read] |
cat /etc/redhat-release |
•/etc/redhat-release |
•Get Red Hat release info |
•Linux |
•/etc/redhat-release [File-Read] |
cat /etc/centos-release |
•/etc/centos-release |
•Get CentOS release info |
•Linux |
•/etc/centos-release [File-Read] |
cat /etc/oracle-release |
•/etc/oracle-release |
•Get Oracle Linux info |
•Linux |
•/etc/oracle-release [File-Read] |
cat /etc/enterprise-release |
•/etc/enterprise-release |
•Get Enterprise Linux info |
•Linux |
•/etc/enterprise-release [File-Read] |
cat /etc/SuSE-release |
•/etc/SuSE-release |
•Get SUSE release info |
•Linux |
•/etc/SuSE-release [File-Read] |
cat /etc/debian_version |
•/etc/debian_version |
•Get Debian version |
•Linux |
•/etc/debian_version [File-Read] |
hostname |
•- |
•Get hostname |
•All supported platforms |
•- |
hostid |
•- |
•Get host ID |
•Solaris |
•- |
zonename |
•- |
•Get zone name |
•Solaris |
•- |
cat /etc/hostname.ce0 |
•/etc/hostname.ce0 |
•Get Solaris hostname |
•Solaris |
•/etc/hostname.ce0 [File-Read] |
lparstat |
•-i |
•Get LPAR info |
•AIX |
•- |
lsattr |
•-El sys0 |
•Get system attributes |
•AIX |
•- |
model |
•- |
•Get HP-UX model |
•HPUX |
•- |
Binary & Path Inventory |
|
|
•All supported platforms |
|
find |
•/bin /sbin /usr/bin /usr /sbin -type f -executable |
•Find executable files |
•All supported platforms |
•/bin, /sbin, /usr/bin, /usr/sbin [File-Read] |
which |
•<command> |
•Find command location |
•All supported platforms |
•- |
ls |
•-l <path> |
•List directory contents |
•All supported platforms |
•Various system directories [File-Read] |
ls |
•<path> |
•List files |
•All supported platforms |
•Various paths [File-Read] |
readlink |
•<file> |
•Read symbolic links |
•All supported platforms |
•Various files [File-Read] |
md5sum |
•<file> |
•Calculate MD5 hash |
•Linux |
•Executable files [File-Read] |
md5 |
•-q <file> |
•Calculate MD5 hash |
•macOS/BSD |
•Executable files [File-Read] |
grep |
•-r <pattern> <path> |
•Search in files recursively |
•All supported platforms |
•Various system files [File-Read] |
awk |
•'<script>' <file> |
•Process text files |
•All supported platforms |
•Various files [File-Read] |
sed |
•'<script>' <file> |
•Edit streams |
•All supported platforms |
•Various files [File-Read] |
Phase 2: Package Management
Only one package manager block is executed, the scan process automatically selects the appropriate one based on the normalized OS identifier determined in Phase 0/1 (e.g.,rpm on RHEL/CentOS/SUSE,
dpkg on Debian/Ubuntu, swlist on HP-UX, pkginfo on Solaris, odmget on AIX, and snap/flatpak where present). All package manager queries run under No-Elevation context.
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
Remote_Files_Accessed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
rpm |
•--querytags |
•Get RPM query tags |
•Linux/AIX/HPUX |
•/var/lib/rpm/ (RPM DB) [File-Read] |
rpm |
•-qa |
•List RPM packages simple |
•Linux/AIX/HPUX |
•/var/lib/rpm/ (RPM DB) [File-Read] |
rpm |
•-qa --queryformat '%{NAME} |
•- |
•- |
•/var/lib/rpm/ (RPM DB) [File-Read] |
dpkg-query |
•-l |
•List DEB packages simple |
•Linux |
•/var/lib/dpkg/status, /var/lib/dpkg/info/ [File-Read] |
dpkg-query |
•-W -f='${db:Status-Abbrev |
•- |
•- |
•/var/lib/dpkg/status, /var/lib/dpkg/info/ [File-Read] |
snap |
•list |
•List Snap packages |
•Linux |
•/var/lib/snapd/state.json [File-Read] |
snap |
•info <package> |
•Get Snap package info |
•Linux |
•/var/lib/snapd/state.json [File-Read] |
flatpak |
•list --columns=name |
•Test Flatpak name column support |
•Linux |
•~/.local/share/flatpak/, /var/lib/flatpak/ [File-Read] |
flatpak |
•list --columns=application,name,size,arch, version,description --app |
•List Flatpak apps |
•Linux |
•~/.local/share/flatpak/, /var/lib/flatpak/ [File-Read] |
flatpak |
•list --columns=application,name,size,arch, version,description --runtime |
•List Flatpak runtimes |
•Linux |
•~/.local/share/flatpak/, /var/lib/flatpak/ [File-Read] |
flatpak |
•list --columns=application,name,size,arch, version,description |
•List Flatpak packages |
•Linux |
•~/.local/share/flatpak/, /var/lib/flatpak/ [File-Read] |
pkginfo |
•-li |
•List Solaris packages |
•Solaris |
•/var/sadm/install/contents, /var/sadm/pkg/ [File-Read] |
swlist |
•-l product -a size -a revision -a architecture -a install_date -a is_patch -a title -a vendor |
•List SDUX packages |
•HPUX |
•/var/adm/sw/ (SD-UX depot) [File-Read] |
odmget |
•product |
•Get AIX product info |
•AIX |
•/etc/objrepos/, /usr/lib/objrepos/ [File-Read] |
odmget |
•-q name=<package> lpp |
•Get AIX LPP info |
•AIX |
•/etc/objrepos/, /usr/lib/objrepos/ [File-Read] |
odmget |
•-q "lpp_id=<id> and ver=<ver> and rel=<rel> and mod=<mod> and fix=<fix>" history |
•Get AIX install history |
•AIX |
•/etc/objrepos/, /usr/lib/objrepos/ [File-Read] |
Phase 3: Hardware Information
This is the first phase where Elevated-First (RunTryElevatedFirst) is used extensively, because tools such as dmidecode, lspci, smbios, prtdiag, and parts of prtconf require root-level access to
low-level system information that is protected by the kernel.
If password-less sudo is unavailable, these commands are silently skipped and the scanner automatically falls back to non-privileged alternatives (lscpu, free -m, cat /proc/cpuinfo, etc.). Only
cat /proc/cpuinfo and cat /etc/filesystems (AIX) explicitly access regular files [File-Read]. By the end of Phase 3, the scanner possesses a complete hardware fingerprint suitable for asset tracking, capacity
planning, and warranty management.
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
Execution Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
lscpu |
•- |
•get CPU info |
•Linux |
•No-Elevation |
cat |
•/proc/cpuinfo |
•Get CPU information |
•Linux |
•No-Elevation |
free |
•-m |
•Get memory info |
•Linux |
•No-Elevation |
dmidecode |
•-t System |
•Get system info |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
dmidecode |
•-t Processor |
•Get processor info |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
dmidecode |
•-t Memory |
•Get memory info |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
dmidecode |
•-t BIOS |
•Get BIOS info |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
dmidecode |
•-t 'System Information' | grep Manufacturer |
•Get system manufacturer |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
/usr/sbin/dmidecode |
•-t <type> |
•Get hardware info (alt path) |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
lspci |
•-v |
•List PCI devices verbose |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
system_profiler |
•SPHardwareDataType |
•Get hardware info |
•macOS |
•No-Elevation |
system_profiler |
•SPSoftwareDataType |
•Get software info |
•macOS |
•No-Elevation |
sysctl |
•-n hw.ncpu |
•Get CPU count |
•macOS |
•No-Elevation |
sysctl |
•-n hw.memsize |
•Get memory size |
•macOS |
•No-Elevation |
bootinfo |
•-r |
•Get real memory |
•AIX |
•No-Elevation |
prtconf |
•- |
•Print configuration |
•AIX |
•No-Elevation |
prtconf |
•-pv |
•Print configuration verbose |
•Solaris |
•Elevated-First |
prtdiag |
•| grep "System Configuration" | awk '{print $3 " " $4}' |
•Get system configuration |
•Solaris |
•Elevated-First |
prtdiag |
•| grep "System Configuration" | awk '{print $8}' |
•Get system model |
•Solaris |
•Elevated-First |
prtdiag |
•-v |
•Print diagnostics |
•Solaris |
•Elevated-First |
smbios |
•-t SMB_TYPE_SYSTEM |
•Get system info |
•Solaris |
•Elevated-First |
smbios |
•-t SMB_TYPE_BIOS |
•Get BIOS info |
•Solaris |
•Elevated-First |
smbios |
•-t SMB_TYPE_CHASSIS |
•Get chassis info |
•Solaris |
•Elevated-First |
/usr/contrib/bin/machinfo |
•- |
•Get machine info |
•HPUX |
•No-Elevation |
getconf |
•-a |
•Get all configuration |
•AIX |
•No-Elevation |
lshal |
•| grep <path> |
•List hardware abstraction |
•Linux |
•No-Elevation (deprecated) |
Phase 4: Storage Management
This phase enumerates mounted filesystems, block devices, physical volumes, logical volumes, and platform-specific disk structures using commands such as df, mount, lsblk, fdisk, lspv, zpool list, zfs list, ioscan, format, prtvtoc, diskutil, smartctl and udevadm. Most commands require Elevated-First due to restricted access to device nodes and raw disk information. File-reading operations (e.g. cat /etc/filesystems on AIX) are marked [File-Read].
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
Remote_Files_Accessed |
Execution Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
df |
•-k |
•Get disk usage |
•All supported platforms |
•- |
•No-Elevation |
mount |
•- |
•Get mounted filesystems |
•All supported platforms |
•- |
•No-Elevation |
stat |
•"/ | awk '/Birth:/ {print $1 \",\" $2 \" \" substr($3,1,5)} /Modify:/ {print $1 \", \" $2 \" \" substr($3,1,5)} /Access:/ {print $1 \",\" $2 \" \" substr($3,1,5)}'" |
•Get filesystem dates |
•Linux |
•/ (root filesystem) [File-Read] |
•No-Elevation |
lsblk |
•-o NAME,SIZE,TYPE,MOUNTPOINT,FSTYPE |
•List block devices |
•Linux |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
fdisk |
•-l |
•List disk partitions |
•Linux |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
pvs |
•-a -v --separator=' |
•- |
•- |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
vgs |
•-a -v --separator=' |
•- |
•- |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
lvs |
•-a -v --separator=' |
•- |
•- |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
smartctl |
•-i <device> |
•Get SMART disk info |
•Linux |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
udevadm |
•info --query=all --name=<device> |
•Get udev device info |
•Linux |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
cat |
•/etc/filesystems |
•Get AIX filesystems |
•AIX |
•/etc/filesystems [File-Read] |
•Elevated-First |
lspv |
•- |
•List physical volumes |
•AIX |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
lspv |
•<device> |
•Get PV details |
•AIX |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
zpool |
•list -H |
•List ZFS pools |
•Solaris |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
zfs |
•list -H |
•List ZFS filesystems |
•Solaris |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
format |
•quit | format |
•List disks via format |
•Solaris |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
prtvtoc |
•<device> |
•Print VTOC |
•Solaris |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
ioscan |
•-funC disk |
•Scan disk devices |
•HPUX |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
diskinfo |
•<device> |
•Get disk info |
•HPUX |
•- |
•Elevated-First |
diskutil |
•list |
•List disks |
•macOS |
•- |
•No-Elevation |
diskutil |
•info <disk> |
•Get disk info |
•macOS |
•- |
•No-Elevation |
Phase 5: Network Configuration
This phase collects network interface configuration and routing information through the commands ifconfig, netstat -rn and ip addr show. All network commands run under Elevated-First context.
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
ip |
•addr show |
•Get network addresses |
•Linux |
ifconfig |
•-a |
•Get all network interfaces |
•Linux/Solaris |
ifconfig |
•<interface> |
•Get specific interface info |
•All supported platforms |
netstat |
•-rn |
•Get routing table |
•All supported platforms |
Phase 6: Process Management
This phase lists running processes and their arguments on all supported Unix platforms using the platform-specific ps variants, pargs and osacript.
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
Execution Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ps |
•-eo pid,user:32 |
•List processes (Linux) |
•Linux |
•Elevated-First |
ps |
•-eo pid,args |
•List processes detailed |
•Linux/AIX |
•No-Elevation |
ps |
•-eo pid,user |
•List processes (basic) |
•AIX/Solaris/macOS |
•Elevated-First |
ps |
•-eo pid,comm -x |
•List processes detailed (HPUX) |
•HPUX |
•No-Elevation |
pargs |
•<pid> |
•Get process arguments |
•Solaris |
•No-Elevation |
osascript |
•-e 'tell application "System Events" to get name of every process' |
•Get macOS processes |
•macOS |
•Script-Execution |
Phase 7: Service Management
The scan identifies configured and active system services across all supported Unix platforms using the native service management frameworks (systemd, SysVInit, SMF, SRC and launchd). All service management commands run under Elevated-First context.
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
Remote_Files_Accessed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
systemctl |
•list-units --type=service |
•List active systemd services |
•Linux |
•/etc/systemd/, /run/systemd/, /usr/lib/systemd/, ~/.config/systemd/ [File-Read] |
systemctl |
•list-unit-files --type=service |
•List installed systemd unit files |
•Linux |
•/etc/systemd/, /run/systemd/, /usr/lib/systemd/, ~/.config/systemd/ [File-Read] |
service |
•--status-all |
•List SysVInit service status |
•Linux |
•/etc/init.d/, /etc/rc.d/ [File-Read] |
chkconfig |
•--list |
•List SysVInit runlevel configuration |
•Linux |
•/etc/rc.d/ [File-Read] |
svcs |
•-a |
•List all SMF services |
•Solaris |
•/lib/svc/manifest/, /etc/svc/, /var/svc/manifest/, /var/svc/profile/ [File-Read] |
svcs |
•-l <service> |
•Detailed information for specific SMF service |
•Solaris |
•/lib/svc/manifest/, /etc/svc/, /var/svc/manifest/, /var/svc/profile/ [File-Read] |
lssrc |
•-a |
•List all SRC subsystems and services |
•AIX |
•– |
launchctl |
•list |
•List all launchd services and agents |
•macOS |
•/Library/LaunchDaemons/, /Library/LaunchAgents/, /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/, ~/Library/LaunchAgents/ [File-Read] |
Phase 8: Container and Virtualization Inventory
The scan detects running containers, images, Kubernetes workloads, Solaris zones and Microsoft SQL Server instances through their respective management utilities.
Command |
Arguments |
Purpose |
Platform |
Remote_Files_Accessed |
Execution Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
docker |
•ps -a --format "table {{.Names}}\t {{.Image}}\t{{.Status}}" |
•List Docker containers |
•Linux |
•/var/lib/docker/ [File-Read] |
•Elevated-First |
docker |
•images --format "table {{.Repository}}\t {{.Tag}}\t{{.Size}}" |
•List Docker images |
•Linux |
•/var/lib/docker/ [File-Read] |
•Elevated-First |
kubectl |
•get nodes |
•List Kubernetes nodes |
•Linux |
•~/.kube/config [File-Read] |
•Elevated-First |
kubectl |
•get pods --all-namespaces |
•List Kubernetes pods |
•Linux |
•~/.kube/config [File-Read] |
•Elevated-First |
zonecfg |
•-z <zone> info |
•Get zone config |
•Solaris |
•/etc/zones/ [File-Read] |
•Elevated-First |
prctl |
•-i zone <zone> |
•Get zone controls |
•Solaris |
•/etc/zones/ [File-Read] |
•Elevated-First |
sqlcmd |
•-S <server> -U <user> -P <pass> -Q "SELECT @@VERSION" |
•Query SQL Server version |
•Linux |
•- |
•Elevated-Last |